Architecture Overview
ECS (Entity Component System) is a design pattern widely used in game development and complex application design, characterized by its flexibility, efficiency, and scalability. EliCS is an implementation of this pattern, offering a streamlined approach to managing entities, components, systems, and queries.
Core Concepts
Entities
Entities are fundamental objects or actors within your application. They are essentially containers for components and do not possess any direct functionality or data.
Types
EliCS provides a set of built-in types for defining component schemas, system configurations, and other data structures. These types ensure consistency, type safety, and efficient data storage.
Components
Components are pure data containers that define the properties or behaviors of entities. They are modular and can be dynamically attached to or detached from entities. Components are automatically registered in a global ComponentRegistry that enables external tool integration and build-time analysis.
Systems
Systems contain the logic of your application. They operate on entities that have specific component configurations, defined through queries.
Queries
Queries are used by systems to efficiently select entities based on their components. EliCS utilizes a bitmasking technique for fast query evaluation.
World
The World is the central orchestrator in EliCS. It manages the lifecycle and interaction of entities, components, systems, and queries.
Example: Building a Game
Imagine we are building a game where players fight against robots and drones. The following example demonstrates the complete workflow—from defining components and creating entities, to developing systems and integrating everything within the World.
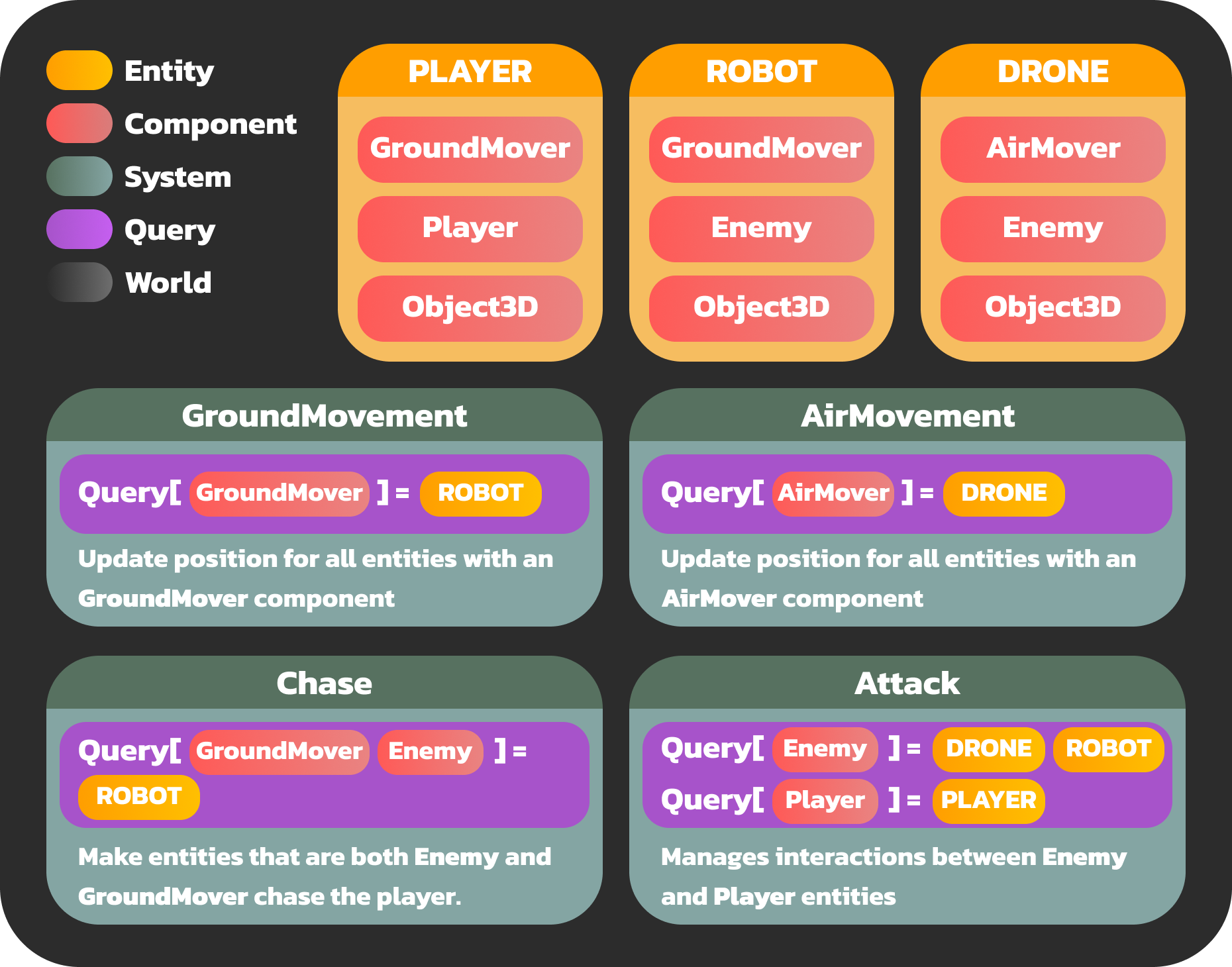
Defining Components:
Components store data that describes specific characteristics of an entity. For our game, we might define:- GroundMover: Indicates the entity can move on the ground.
- AirMover: Indicates the entity can move through the air.
- Enemy: Identifies the entity as an enemy.
- Object3D: Contains the Object3D data for rendering.
Creating Entities:
Entities are objects in the game world, defined by the components they possess. For our game:- Robot: Has the
GroundMover,Enemy, andObject3Dcomponents. - Drone: Has the
AirMover,Enemy, andObject3Dcomponents. - Player: Has the
GroundMoverandObject3Dcomponents.
- Robot: Has the
Defining Systems:
Systems implement the logic that acts on entities with specific components. In our example:- GroundMovement System: Moves all entities with a
GroundMovercomponent (e.g., Player, Robot). - AirMovement System: Moves all entities with an
AirMovercomponent (e.g., Drone). - Chase System: Makes entities that are both
EnemyandGroundMover(e.g., Robot) chase the player. - Attack System: Manages interactions between
EnemyandPlayerentities.
- GroundMovement System: Moves all entities with a
World Integration and Execution Cycle:
Register components and systems with the World. This step initiates the execution cycle:- The World creates entities, attaches components, and registers systems.
- The execution cycle begins as the World updates all systems in each frame or tick, processing entity interactions and game logic.